Researcher uses decomposition fungi to create patterns in wood
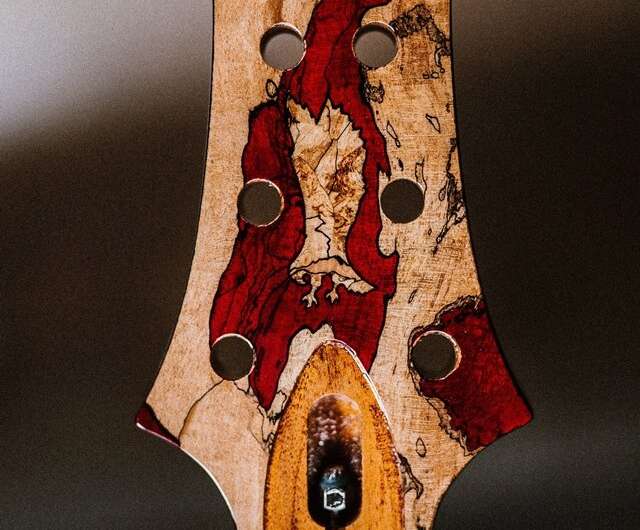

Fungi that decompose tree trunks can conjure up real works of art in wood. In nature, however, the decay-causing fungi not only decorate the tree, but also destroy it. Empa researchers are now teaching the fungi how to draw. The result: upscale marbled wood that can be processed into design furniture or musical instruments.
Sometimes there is true beauty to be discovered in very unusual places. Like Phoenix from the ashes, the coveted truffle beech is made from rotting wood on the forest floor. Uniquely patterned, it has been a sought-after as a raw material for furniture production since antiquity. However, the search for natural truffle beeches is tricky. Even those who deliberately leave tree trunks to rot in the forest have to wait years before they can hope to obtain wood that is decorated with fungal-induced patterns and, furthermore, still usable. Empa researchers have now developed a technology, with which hardwoods such as beech, ash and maple can be specifically treated with fungal cultures so that the patterns in the wood can be controlled.
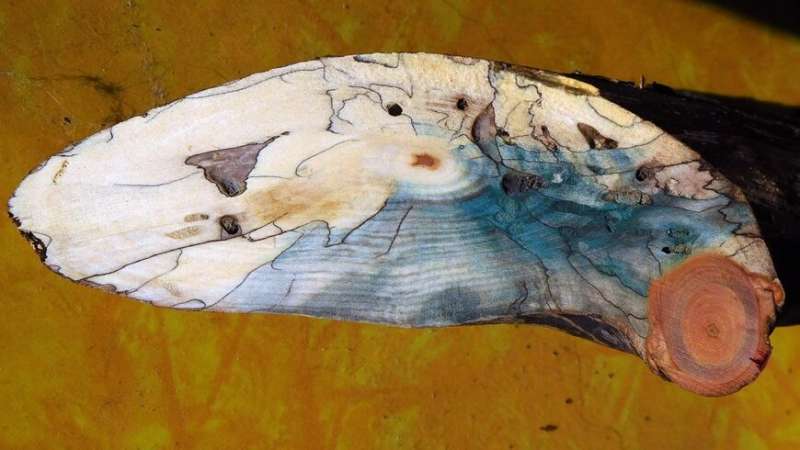

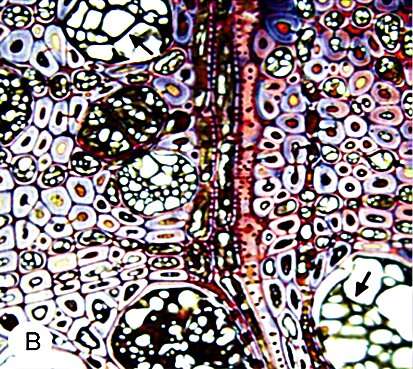
The fine black lines running through the wood are the traces of a battle. Sometimes they meander turbulently towards each other and separate small plots with lightened background. In other places, the dark drawings flow calmly as if they wanted to remind us of a boundary that none of the participants likes to cross: Fungi that have fought in a battle for territory and resources in the wood clearly separate themselves from each other with pigmented lines. With these demarcation lines, the fine threads of the fungal community not only protect their colony from other fungi – the black boundary also ensures that bacteria and insects stay away and the habitat retains an ideal amount of moisture.

"We were able to identify fungi growing in nature and analyze them in the laboratory to select those with the most favorable properties as wood finishers," says Hugh Morris, a scientist in Empa's Applied Wood Materials lab in St. Gallen. For example, the brittle cinder fungus and the Turkey-tail when matched with each other leave black lines caused by the pigment melanin and at the same time bleach the surrounding wood thanks to the fungal enzyme laccase. "This creates a pattern with a particularly strong contrast in the wood" explains Hugh Morris.
Depending on the combination of fungal species, the lines are wild and impetuous or almost geometric. The researcher is convinced that the fungi can even, in time, be trained to write words in the wood. The gentle bite of the fungi that are used in the Empa laboratory is particularly favourable: Despite their pronounced talent for drawing, the selected candidates hardly gnaw their substrata. "Although fungi generously supply the wood with pigments, the wood retains its stability and shape," says Hugh Morris.
Magic of Nature: Spalted Wood
However, the fact that the artistic process can be controlled and geared towards the desired result is not only owing to the type of fungus, the researchers also developed a process, with which the wood is ready for processing within weeks. One of the reasons for this rather fast processing is that the selected fungal species are able to grow in the wood with considerably lower moisture levels. This means that the raw material does not have to be dried long, costly or energy-intensive before being processed into furniture.
Together with the industry partner Koster Holzwelten AG, the researchers are now in the process of implementing an efficient and ecologically sustainable production method. This also includes the use of regional wood. "Beech wood is a hardwood that is common in Switzerland but appears uninteresting to furniture designers," explains

With marble wood from local beech trees, however, it is possible to offer sought-after products on the Swiss timber market with an annual volume of around 3 billion Swiss francs.
In addition to furniture, parquet floors and kitchen fronts, marble wood can also be used for decorative objects and musical instruments. Unique pieces have always been created from patterned wood. With the new technology, spalted wood can now be produced faster, more sustainably and with the desired marbling.
-
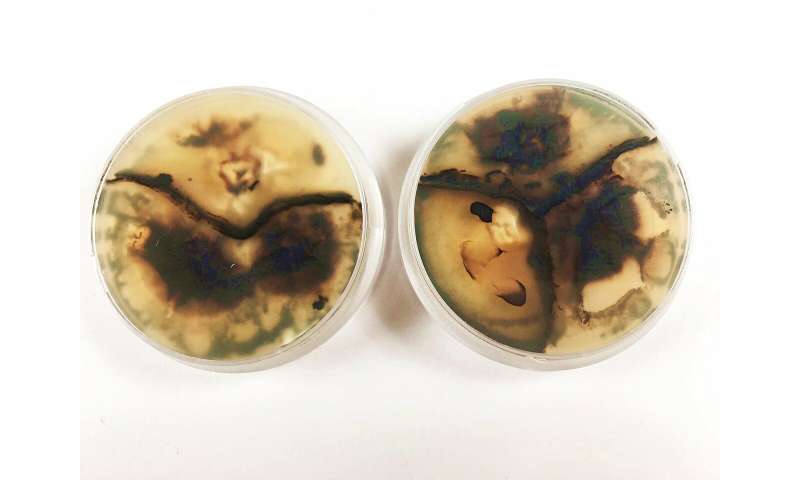
In the laboratory, Empa researchers have selected and analyzed those fungal cultures that can draw the most interesting lines. Credit: Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology -
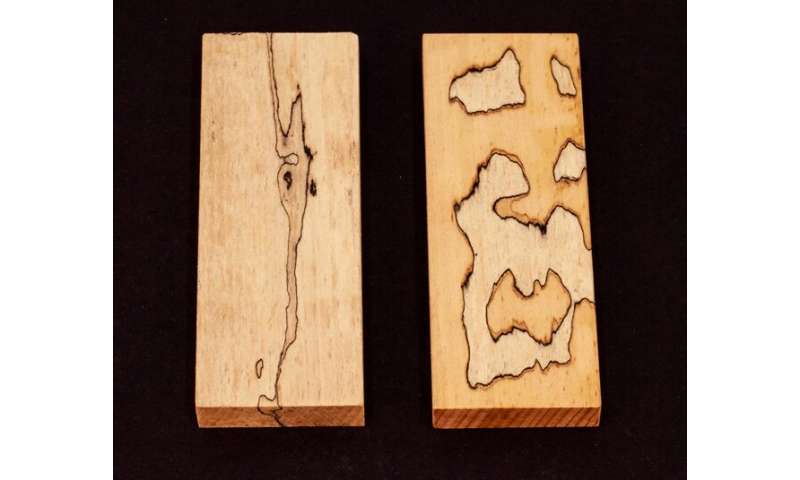

Marbled wood from the lab: Depending on the kind of fungi used, the course of the pattern in the wood can be controlled. Credit: Empa
More information: H Morris. Spalted wood and the dark side of fungi; INK Quarterly (2018)